Tracing curves of a power transmitting DHT
 Finding triode curves for the 4-65a valve has been a challenging task. There are some available from a Spice simulation which I couldn’t get hold of the model, so when I finished the curve tracer, it was the right time to take on this challenge. My curve tracer is not capable of handling this valve as I don’t have the appropriate socket and also the anode and grid drivers are limited to:
Finding triode curves for the 4-65a valve has been a challenging task. There are some available from a Spice simulation which I couldn’t get hold of the model, so when I finished the curve tracer, it was the right time to take on this challenge. My curve tracer is not capable of handling this valve as I don’t have the appropriate socket and also the anode and grid drivers are limited to:
- Anode voltage sweep range: 0-330V
- Anode maximum current: 100mA
- Grid voltage sweep range: -80V – +15V
With this constraining factors in mind, I decided to build a test jig for the 4-65a. The jig had only a grid stopper resistor (10kΩ), a screen stopper (100Ω) and ferrite beads in the anode and grid as well. When traced first set of curves got very disappointed with a double tracing for each anode curve which made me suspect that the valve was oscillating somehow due to long cables,etc. Its transconductance is below 3 mA/V, so shouldn’t be that problematic. I remember tracing 6e5p,6C45 and E180F being a real challenge for the tester due to its high transconductance.
Here is a sample of the double tracing from the first test:
 I tried many things with cables, stoppers and ferrite beads with no success. Suddenly the penny dropped and looked at the old DC raw supply I was using. I had only one capable of providing 6.3V @ 3.5A. And it’s regulation was appalling. The ripple was clearly a potential candidate for this image distortion. If ripple was high enough, it will modulate the cathode and therefore Vgk. Ripple frequency is same as refresh frequency of the curves (i.e. 100Hz).
I tried many things with cables, stoppers and ferrite beads with no success. Suddenly the penny dropped and looked at the old DC raw supply I was using. I had only one capable of providing 6.3V @ 3.5A. And it’s regulation was appalling. The ripple was clearly a potential candidate for this image distortion. If ripple was high enough, it will modulate the cathode and therefore Vgk. Ripple frequency is same as refresh frequency of the curves (i.e. 100Hz).

My test jig was modified to include a hum cancellling pot. as shown in the following diagram. I added a 100Ω and a 22mF electrolytic.
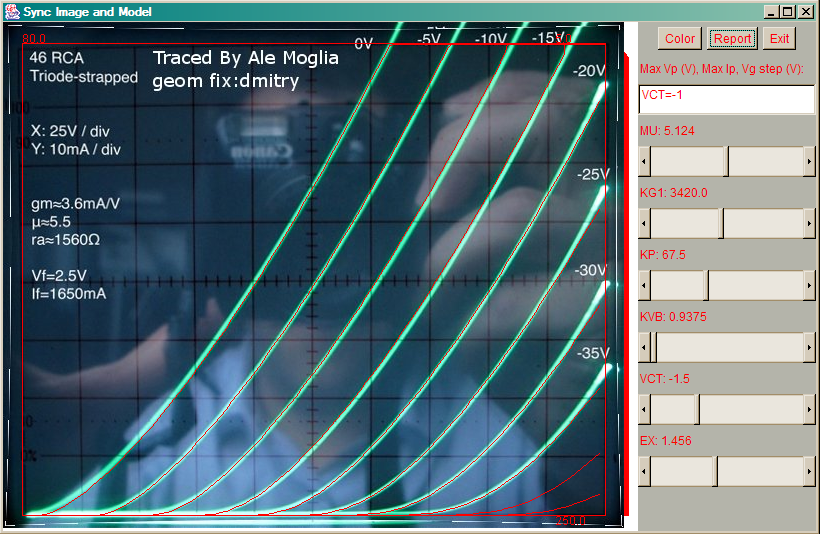
Tracing curves again then was a success. I had to trim the pot to cancel the hum and alas, the curves were very neat.
The addition of the grid stopper limited the grid current closer to 0V or above. Therefore the 0V curve gets packed closer to the following one (i.e. -5V). This can be clearly seen when the Spice model is generated

My tracer has not been designed to trace positive grid curves, so the current capability of the grid driver at positive grid voltages is limited. I need to modify the circuit, but it will have to wait as I have already spent too much time in this tracer so far!
After playing a while with Dmitry’s tool, I came up with a very reasonable model for the 4-65a. I’m sure it can be optimised, but for a couple of hours work, I’m very happy with the results…